Table of Contents
Toggle
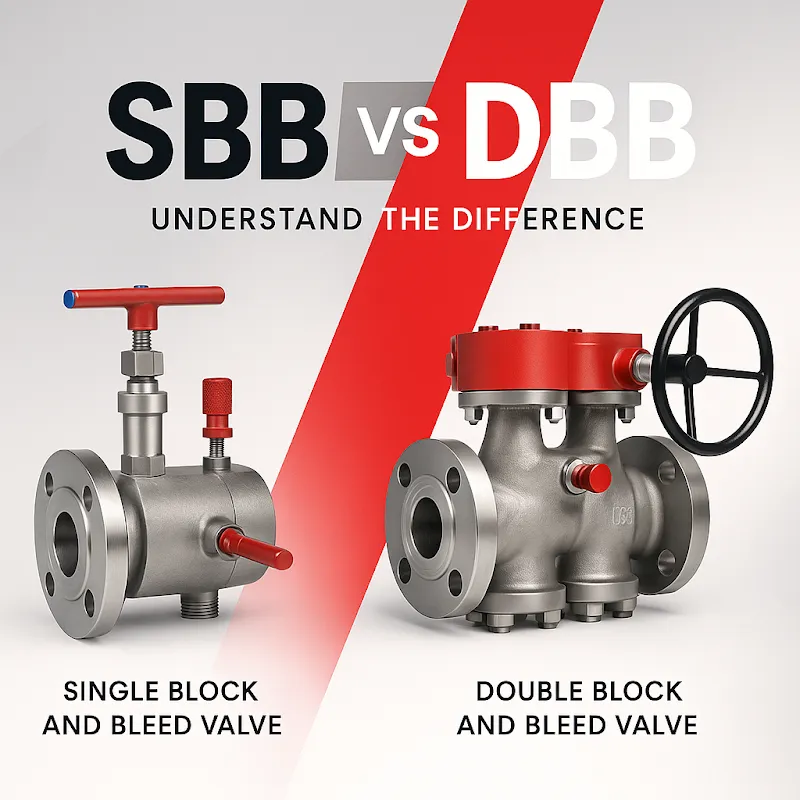
The main difference between a single block and bleed valve vs double block and bleed valve is the number of isolation points. An SBB valve uses one block valve and a bleed port for basic isolation, while a DBB valve uses two block valves and one bleed valve, offering higher safety and complete isolation for critical systems.
SBB vs. DBB in Valves
When discussing SBB (Single Block and Bleed) and DBB (Double Block and Bleed) in the valve context, the focus is on isolation and drainage capability. Both are used in process piping and instrumentation, but their configurations and safety levels vary significantly.
| Feature | Single Block and Bleed (SBB) Valve | Double Block and Bleed (DBB) Valve |
| Configuration | One block valve with a bleed port | Two block valves with a bleed valve between |
| Isolation Level | Single-point isolation | Dual-point isolation with superior sealing |
| Safety | Moderate; not for hazardous media | High; suited for flammable and toxic media |
| Application | Lower-risk, single-direction systems | High-risk environments requiring positive isolation |
In short, SBB is acceptable where moderate safety suffices, while DBB is mandatory in environments where failure is not an option.
SBB vs. DBB in Electrical Switchgear
Outside of valves, SBB and DBB also apply to high-voltage substations in the form of busbar layouts:
| Feature | Single Busbar (SBB) Switchgear | Double Busbar (DBB) Switchgear |
| Configuration | All lines connected to one busbar | Two busbars allow switching between them |
| Reliability | Lower—failure shuts down system | High—load can transfer during maintenance |
| Cost | Simpler and cheaper | More complex, higher cost |
| Application | Small substations or less redundancy | Large, critical plants and grids |
This shows how the principle of redundancy vs. simplicity applies in both piping and power systems.
What is the Purpose of a Double Block and Bleed Valve?
The primary purpose of a double block and bleed valve is to provide positive isolation. The two block valves ensure that even if one seal fails, the second prevents flow. The bleed valve safely vents any trapped media, protecting workers and equipment from leaks or pressure buildup.
DBB valves are widely used in oil & gas, petrochemical, and power generation industries, where the consequences of leakage can be severe. For a deeper breakdown, see our guide on understanding double block and bleed valve.
When Would You Use the Double Block and Bleed Method?
The double block and bleed method is used in scenarios where absolute safety is needed during maintenance, repair, or shutdowns. Common examples include:
- Offshore drilling rigs handling flammable hydrocarbons
- Chemical reactors with toxic contents
- High-pressure pipelines transporting natural gas
- Power plant steam systems where overpressure is a risk
In each case, DBB systems reduce leakage, protect workers, and comply with strict safety requirements.
Is Double Block and Bleed Required by OSHA?
OSHA does not specifically mandate DBB valves in every case. However, it recognizes DBB systems as a best practice for isolation under Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) and confined space standards. According to OSHA:
- LOTO best practice: DBB is an accepted method of isolating hazardous energy.
- Confined spaces: Defined in Permit-Required Confined Space standards as a valid isolation method.
- Employer responsibility: Employers must choose safe, positive isolation systems. DBB fulfills this requirement.
So, while not mandatory in all industries, DBB valves are often the safest and most OSHA-aligned choice.
Key Differences Summarized
The essence of single block and bleed valve vs double block and bleed is:
- SBB valve: One block + one bleed. Provides moderate isolation for low-risk systems.
- DBB valve: Two blocks + one bleed. Provides superior isolation, preventing leaks in high-risk, critical environments.
DBB valves are also available in compact, integrated designs that reduce space and leak points. If you’d like a detailed look at design differences, see our comparison of DBB vs. DIB valves.
FAQ
What is the difference between a DBB valve and a single block valve?
A DBB valve has two block valves and a bleed, offering dual isolation. A single block valve provides only one barrier, making it less safe for high-risk operations.
What is the purpose of a double block and bleed valve?
To provide positive isolation and a safe way to vent trapped fluids, ensuring no leakage reaches downstream systems.
When would you use the double block and bleed method?
In oil & gas, chemical plants, or power stations where hazardous fluids or gases must be safely isolated for maintenance.
Is double block and bleed required by OSHA?
Not strictly required, but OSHA recognizes DBB as a best practice for safe isolation, especially under LOTO and confined space regulations.
Conclusion
Choosing between an SBB and a DBB valve depends on risk level and application. SBB valves are fine for non-critical isolation, while DBB valves are essential in high-risk systems where safety is paramount. Understanding these differences ensures compliance, safety, and system reliability. At Gowin, we specialize in both single block and bleed and double block and bleed solutions. With 16+ years of expertise, international certifications, and custom R&D, we help industries worldwide meet their flow control needs.